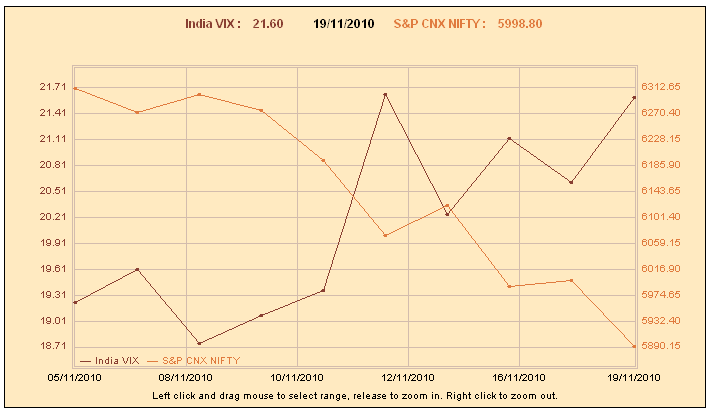
India VIX is India’s volatility Index which is a key measure of market expectations of near-term volatility conveyed by NIFTY stock index option prices. This volatility index is computed by NSE based on the order book of NIFTY Options. For this, the best bid-ask quotes of near and next-month NIFTY options contracts which are traded on the F&O segment of NSE are used. India VIX indicates the investor’s perception of the market’s volatility in the near term i.e. it depicts the expected market volatility over the next 30 calendar days. Higher the India VIX values, higher the expected volatility and vice-versa. NSE will also start derivatives based on India VIX. Most probably NSE will come out with India Vix Futures first followed by India Vix options as had been done by the CBOE in the past.
India VIX – Live (Real Time) Chart and Quotes
India VIX Live Chart –
http://vix.co.in/indiavix/live-chart
Meaning of Volatility Index – Volatility Index (VIX) is a key measure of market expectations of near term volatility. As we understand, volatility implies the ability to change. Thus when the markets are highly volatile, market tends to move steeply up or down and during this time volatility index tends to rise. Volatility index declines when the markets become less volatile. VIX is sometimes also referred to as the Fear Index because as the volatility index (VIX) rises, one should become fearful or I would say careful as the markets can move steeply into any direction. Worldwide, VIX has become an indicator of how market practitioners think about volatility. Investors use it to gauge the market volatility and make their investment decisions.
It is important to understand that Volatility Index is different from a price index such as NIFTY or Sensex. The price index measure the direction of the market and is computed using the price movement of the underlying stocks where as Volatility Index measures the dispersion or variance or change and is computed using the order book of the underlying index options and is denoted as an annualized percentage.
VIX was first introduced by the Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE) as the volatility index for the US markets in 1993 and it was based on S&P 100 Index option prices. The methodology was revised in 2003 and the new volatility index was based on S&P 500 Index options. CBOE also introduced VIX options and VIX Futures.
NSE has also started real time dissemination of India VIX which is one step towards introduction of India VIX derivatives. India VIX futures and India VIX options can be used to hedge the risk of market volatility.
Further Readings
India Volatility Index Calculations
How India Vix is related to Nifty Options